니켈 및 니켈 합금
Material Introduction
니켈(Ni)은 주기율표 10족(IIb)에 속하는 금속 원소로, 은백색의 광택을 지닌 금속입니다. 니켈(Ni)은 우수한 강도와 내식성을 특징으로 하며, 특히 뛰어난 내열성과 내식성 덕분에 다양한 산업 분야에서 널리 활용됩니다. 또한, 화학적으로 비교적 안정적이며, 공기 중에서 산화막을 형성하여 부식으로부터 자체 보호됩니다. 그 결과, 니켈(Ni)은 스테인리스강, 전기 배터리, 전자기기 등에 필수적인 합금의 핵심 성분으로 사용됩니다. 더불어, 높은 전기전도도와 열전도성을 갖추고 있어 전기 응용 분야에서도 중요한 역할을 하며, 이외에도 촉매로 작용하여 화학 반응을 촉진하는 데 활용됩니다.
Physical Properties | |
Phase | Solid |
Std Atomic Weight | 58.6934 |
Melting point / °C | 1728 K (1455 °C, 2651 °F) |
Boiling point / °C | 3003 K (2730 °C, 4946 °F) |
Density / g.cm¯³ | 8.908 g/cm3 |
Crystal structure | face-centered cubic(fcc) |
ElecCtrical Resistivity | 69.3 nΩ·m (at 20 °C) |
Thermal expansion | 13.4 µm/(m·K) (at 25 °C) |
Thermal conductivity | 90.9 W/(m·K) |
General Properties | |
Symbol | Ni |
Numberl | 28 |
Element Category | Transition Metal |
ASTM Standard Specifications | |
ASTM B160 | |
Products
Pure Nickel
Nickel 200
Physical Properties
Speccifications
Density | Melting |
8.89 g/cm³ | 1435-1446℃ |
Grade | UNS | W.Nr |
Nickel 200 | N02200 | 2.4060 |
Chemical Composition
Grade | % | Ni | Fe | C | Mn | Si | Cu | S |
Nickel 200 | Min | Bal. | ||||||
Max | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.01 |
Nickel 200 Mechanical Properties (Min Value at 20°C)
Material | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength (0.2% Offset) | Elongation in 2”(%) | ||
Nickel 200 | ksi | MPa | ksi | MPa | |
55-75 | 380-520 | 15-30 | 105-210 | 55-40 | |
Nickel 201
Speccifications
Mechanical Property Requirements
Grade | GB/T | UNS | W.NrA | JIS |
Nickel201 | N02201 | N02200 | 2.4060 | 2.4061 |
Ultimate Tensile | Yield Strength (0.2% OS) | Elongation. | |
Min | 50 KSi | 10 KSi | 40 |
Min | 345 MPa | 70 MPa |
Chemical Composition
Grade | % | Ni+Co | Cu | Fe | Mn | C | Si | S |
Nickel 201 | Min | 99 | ||||||
Max | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.35 | 0.01 |
Grade | Denisty | Melting Point | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength | Elogation | Standard |
Monel K-500 | 8.05 | 1300-1350 | ≥1100 | ≥790 | ≥20 | ASTM B865 |
Monel 400 | 8.83 | 1300-1350 | ≥480 | ≥170 | ≥30 | ASTM B164 |
Inconel 625 | 8.44 | 1290-1350 | ≥760 | ≥345 | ≥30 | ASTMB443 |
Inconel 600 | 8.43 | 1370-1430 | ≥585 | ≥240 | ≥30 | ASTM B168 B166 |
Inconel 718 | 8.24 | 1260-1320 | ≥965 | ≥550 | ≥30 | ASTMB637 |
Inconel X-750 | 8.25 | 1395-1425 | ≥930 | ≥515 | ≥30 | ASTMB637 |
Hastelloy B3 | 9.22 | 1330-1380 | ≥860 | ≥420 | ≥53.4 | ASTMB335 |
Hastelloy-B2 | 9.20 | 1330-1380 | ≥745 | ≥325 | ≥40 | ASTMB335 |
Hastolloy C-276 | 8.90 | 1325-1370 | ≥758 | ≥363 | ≥62 | ASTMB574 |
Incoloy 800 | 8.00 | 1350-1400 | ≥500 | ≥210 | ≥35 | ASTMB409 |
Incoloy 800 | 8.10 | 1370-1400 | ≥550 | ≥250 | ≥35 | ASTMB424 |
Application | ||||||
With the industrial level improving, Nickel based alloy widely used in many industry fields such as Desalination, Wastewater treatment, Atomic power, Chemical equipment and Salt manufacturing. | ||||||
Precision Alloy
Kovar / 4J29

Speccifications
ASTM | UNS | W.Nr |
F15 | K94610 | 1.3981 |
Coefficient Of Linear Expannsion
Grade | a/10-6·K-1 | ||
Kovar | 200-300℃ | 20-400℃ | 20-450℃ |
/ | 4.6-5.2 | 5.1-5.5 | |
Chemical Composition
Grade | % | Ni | Cr | Fe | Co | Cu | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Mo |
Kovar | Min | 28.5 | Bal. | 16.8 | ||||||||
Max | 29.5 | 0.2 | 17.8 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.20 |
Invar 36 / 4J36

Speccifications
UNS | W.Nr |
K93600 | 1.3912 |
Mechanical Properties (Minimum Value at 20℃)
Tensile Strength σb/MPa | Yield Strength σp0.2/MPa | Elongation σ5 /% |
490 | 240 | 42 |
Chemical Composition
Grade | % | Ni | Fe | C | Mn | Si | P | S |
Invar 36 | Min | 35 | Bal. | 0.2 | ||||
Max | 37 | 0.05 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
Other Products
Grade | C | S | P | Mn | Si | Ni | Mo | Cu | Fe |
1J50 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.15-0.3 | 49-50.5 | ≤0.2 | Bal. | |
1J50 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 | 0.6-1.1 | 0.3-0.5 | 78.5-80 | 3.8-4.1 | 0.02 | Bal. |
1J85 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.15-0.3 | 79-81 | 4.8-5.2 | ≤0.2 | Bal. |
Plate & Sheet
Item | Nickel plate, nickel sheet |
Standard | ASTMA162,GB/T2054,DIN177502002,ASTM B127, |
ASTM B435,ASTMB582,ASTM B575, ASTM B168, | |
ASTM B443, ASTM B463,ASTM B626,ASTM B536,etc | |
Material | N7,N5,N4,N1,NO2200,NO2201,NO4400,NO6002,NO6022,NO6030,NO6455,NO6600, |
NO8800, NO8810, NO8825, Etc | |
Thickness | 0.1-100mm |
Width | 100-2500mm |
Length | 2m, 2.44m, 3m, or as required |
Application | 1) 70% Ni was used for produce stainless steel and heat resistance steel |
2) 15% of the Ni in the world was used as electroplating. | |
3) Used as catalyst in oil industry | |
4) Ni is one of the chemical source of energy ,the need material for battery | |
5) Used to make pigment ,dye,ceramic, and ferrite. |
Rod
Grade | Process | Dia(mm) | Dia. allowable tolerance(mm) | Specification | ||
Drawing | Forging | Grinding or machining | ||||
N4,N5 | Hot forging (rolling) + Lathing (grinding) | 0.8~2.5 | – | ±2% | ±0.03 | GB4435-84 |
N6,N7 | >2.5~5.0 | – | ±0.1 | ASTM B160-93 | ||
N02200 | >5.0~8.0 | 0 | ±0.15 | DIN17740 | ||
N02201 | >8.0~10 | 0 | ±1.0 | ±0.3 | ||
>10~20 | 0 | ±1.5 | ±0.4 | |||
>20~30 | 0 | ±2.0 | ±0.5 | |||
>30~50 | 0 | ±2.5 | ±0.6 | |||
>50~80 | – | ±3.0 | ±0.8 | |||
>80~100 | – | ±3.5 | ±1.1 | |||
>100~120 | – | ±5.0 | ±1.3 | |||
>120~160 | – | ±5.0 | ±1.8 | |||
>160~200 | – | ±6.5 | ±2.0 | |||
>200~500 | – | ±7 | ±2.5 | |||
Tube
Grade | Technology | Status | Size(OD×WT×Lmm) | Specification |
N4, N5, | Hot rolling | MY | Φ5-110×1.0-10×2000-9000 | ASTM B161 |
N6, N7, | ASTM B162 | |||
N02200,N02201 | GB/T2882 | |||
Weld | MY | Φ89-1000×3.0-10×1000-9000 | GB/T2054 |
Wire
Grade | Status | Size | Specification |
N4,N5,N6,N7, | M Y | 0.5-6.0mm | AWSA 5.16 |
NCu28-2.5-1.5 | ASTM B164 | ||
NCu40-2-1 | DIN17740 | ||
NCu30 |
Wire Mesh
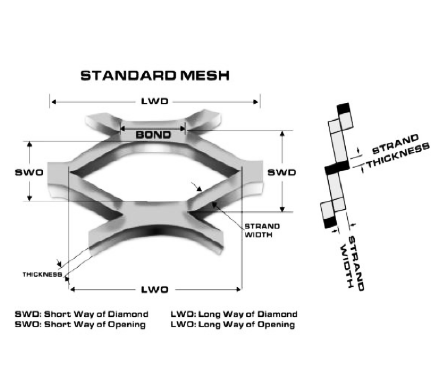
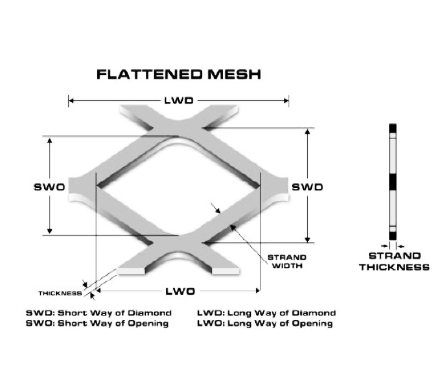
Specification of Nickel Wire Mesh for Battery
material | pure nickel wire or grade N4 N6 N8 wire |
mesh counts | 1-300mesh / inch |
wire diameter | 0.025-2.03mm |
technique of mesh | weaving type mesh,knitted type mesh |
weaving type | plain woven |
sample | ok and available |
Specification Form
Mesh/Inch | Wire Gauge SWG | Aperture mm |
3 | 14 | 6.27 |
4 | 16 | 4.27 |
5 | 18 | 3.86 |
6 | 18 | 3.86 |
8 | 20 | 2.26 |
10 | 20 | 1.63 |
20 | 30 | 0.95 |
30 | 34 | 0.61 |
40 | 36 | 0.44 |
50 | 38 | 0.36 |
60 | 40 | 0.30 |
80 | 42 | 0.21 |
100 | 44 | 0.172 |
120 | 44 | 0.13 |
150 | 46 | 0.108 |
160 | 46 | 0.097 |
180 | 47 | 0.09 |
200 | 47 | 0.077 |
Section of electrozer cell
40 mesh active nickel mesh
Elastic Net
Wire Mesh Belt
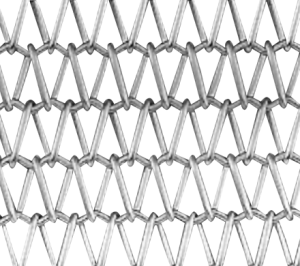
B -Type Belt
- It is an extremely common type of mesh belt, and it has the advantage of low overall cost and tensile strength of more than 50% stronger than that of S-type due to its structure.
- 2The spiral is alternated from side to side, and the uneven connecting pins are mated. This well-balanced structure voluntarily corrects the meandering that may occur during belt operation and corrects the tendency of the belt to slip. In addition, the transverse connecting pins strengthen the elongation force, minimizing the shrinkage of the belt and strengthening the structure.
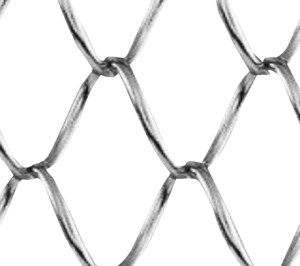
S -Type Belt
- As an extremely simple tissue, it is suitable for cheap and light work, and it has the disadvantage of bending in an S-shape, so it should be used with special attention to tensile strength.
- The 2S-Type consists of several intersecting spirals bent left and right, with the leading spiral inserted inward. The length of the intersected sections is generally determined by the specifications of the drive rollers.
G -Type Belt
- The G-Type is the same as the B-Type except for the narrow pitch of the spiral, but the left side of the helix is alternately assembled and the connecting pins are inserted to distribute the safety strength to the left and right. The intersection of the cotton spiral is narrow, and the neck trunk is inevitably smaller. Unlike the B-Type, the connecting pins are straight and not uneven.
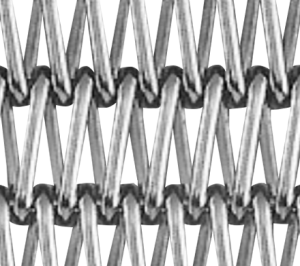
DB -Type Belt
- DB-Type (Double Balanced) is a structure in which the tensile force is doubled by assembling the spiral in a double layer. It can also make the pitch smaller, making it versatile.
- The structure of DB-Type, which is a variant of the 2B-Type, consists of a set of spirals that are misaligned from side to side. This structure has a greater tensile strength than the typical B-Type specification and is used extensively in a variety of driving environments.
- 3However, because of its relatively high cost, DB-Type is mainly considered in high-temperature environments.
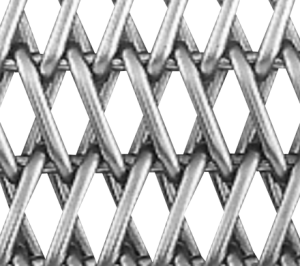
H -Type Belt
- The H-Type has a smooth and dense structure, with spirals bent from side to side that are firmly interlocked with each other, connected by three or more straight rods.
- 2The robust and compact structure makes it ideal for transporting unstable or heavy items as well as very small and delicate products.


